Description
Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate) is a medication that is commonly used in Post Cycle Therapy (PCT), particularly after the use of anabolic steroids or other performance-enhancing drugs that suppress natural testosterone production.
What is Clomid?
Clomid is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). It works by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, which is the part of the brain that helps regulate hormone production. By doing so, Clomid stimulates the release of gonadotropins (LH and FSH) from the pituitary gland, which in turn signals the testes to begin producing testosterone again.
How Does Clomid Work in Post Cycle Therapy (PCT)?
When athletes or bodybuilders use anabolic steroids, they often experience a suppression of natural testosterone production. This happens because the body detects the elevated testosterone levels caused by steroid use and reduces its own production. After stopping steroid use, it can take time for the body to return to normal testosterone levels.
Clomid is used in PCT to help kick-start the body’s natural testosterone production after a steroid cycle. Here’s how it helps:
-
Restores natural testosterone production: Clomid increases the levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulate the testes to produce testosterone.
-
Prevents estrogen-related side effects: By blocking estrogen receptors, Clomid prevents estrogen from interfering with testosterone production, which can happen after the cessation of steroid use.
Why is Clomid Used in PCT?
-
Rebooting natural testosterone production: After an anabolic steroid cycle, testosterone levels are usually low. Clomid helps restart natural testosterone production, which is essential for maintaining muscle mass, libido, and overall well-being.
-
Preventing estrogen rebound: Some anabolic steroids can increase estrogen levels in the body, which can lead to side effects like gynecomastia (breast tissue development in men). Clomid helps block estrogen activity, reducing the risk of these side effects during PCT.
-
Reducing side effects of low testosterone: After a steroid cycle, athletes may experience symptoms of low testosterone (e.g., fatigue, depression, decreased libido). Clomid helps mitigate these symptoms by stimulating the natural production of testosterone.
Clomid Dosage in PCT
Clomid is typically taken for about 4 to 6 weeks during PCT. The dosage may vary based on the individual’s needs and the specifics of the steroid cycle, but a common dosing regimen is:
-
First 2 weeks: 100 mg per day
-
Next 2 weeks: 50 mg per day
-
After completing the cycle, Clomid can be discontinued, but the duration may be adjusted based on how the individual is responding to therapy.
Side Effects of Clomid
Although Clomid is generally considered safe when used properly, it can cause side effects, including:
-
Mood swings: Some users report irritability, mood swings, or depression.
-
Vision changes: Some people may experience visual disturbances or blurred vision.
-
Hot flashes: Like other hormone-related medications, Clomid can cause hot flashes.
-
Gastrointestinal discomfort: Nausea, bloating, and other digestive issues are possible.
-
Possible hormonal imbalance: In rare cases, Clomid can lead to further hormonal imbalances if used improperly.
Conclusion
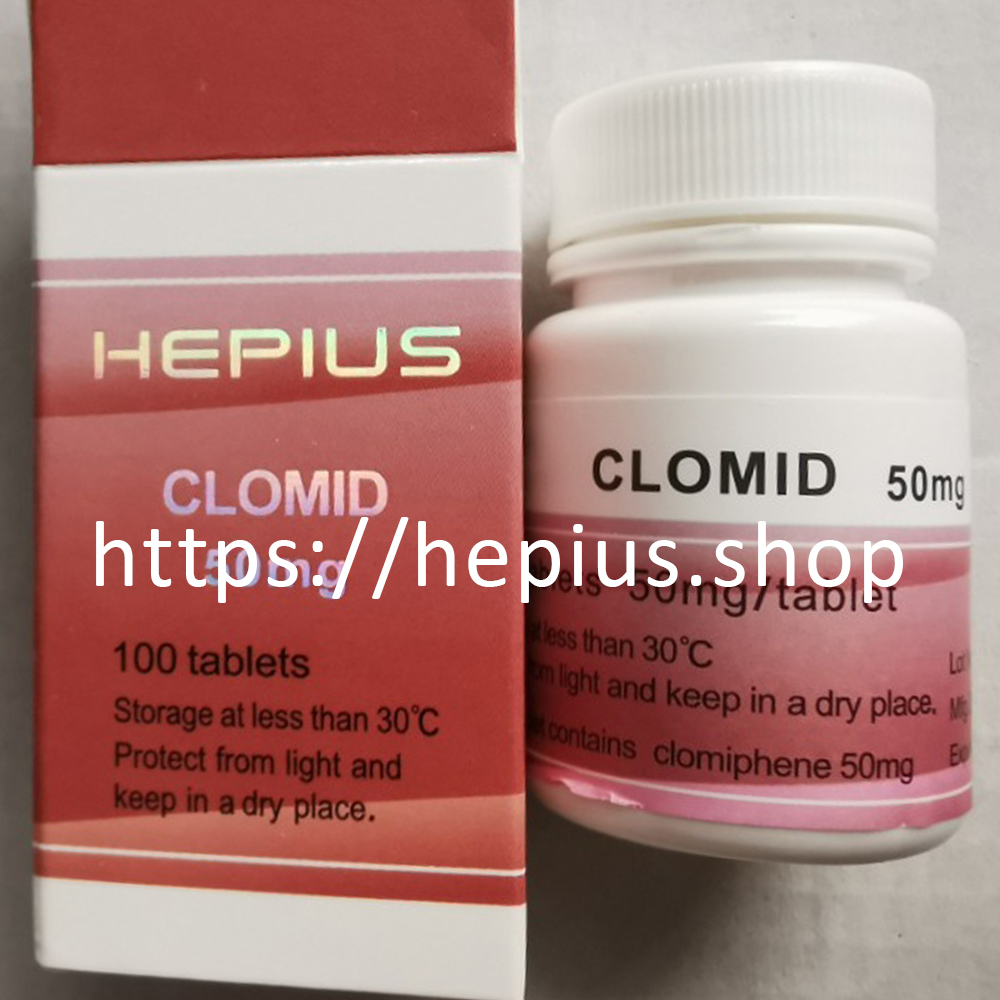
Clomid is a valuable tool in Post Cycle Therapy (PCT), helping athletes restore natural testosterone levels after a cycle of anabolic steroids or other performance-enhancing drugs. It promotes the production of testosterone by stimulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and prevents estrogenic side effects that can occur when steroid use is discontinued. However, as with any medication, it should be used cautiously and ideally under the supervision of a healthcare professional.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.